LoRaWAN Network Server
The Network Server (NS) is a critical component of the LoRaWAN infrastructure, provide de-duplication, radio control (Adaptive Data Rate – ADR), and forwarding encrypted application data up to the Application Server (uplinks) and down to the end-nodes (downlinks).
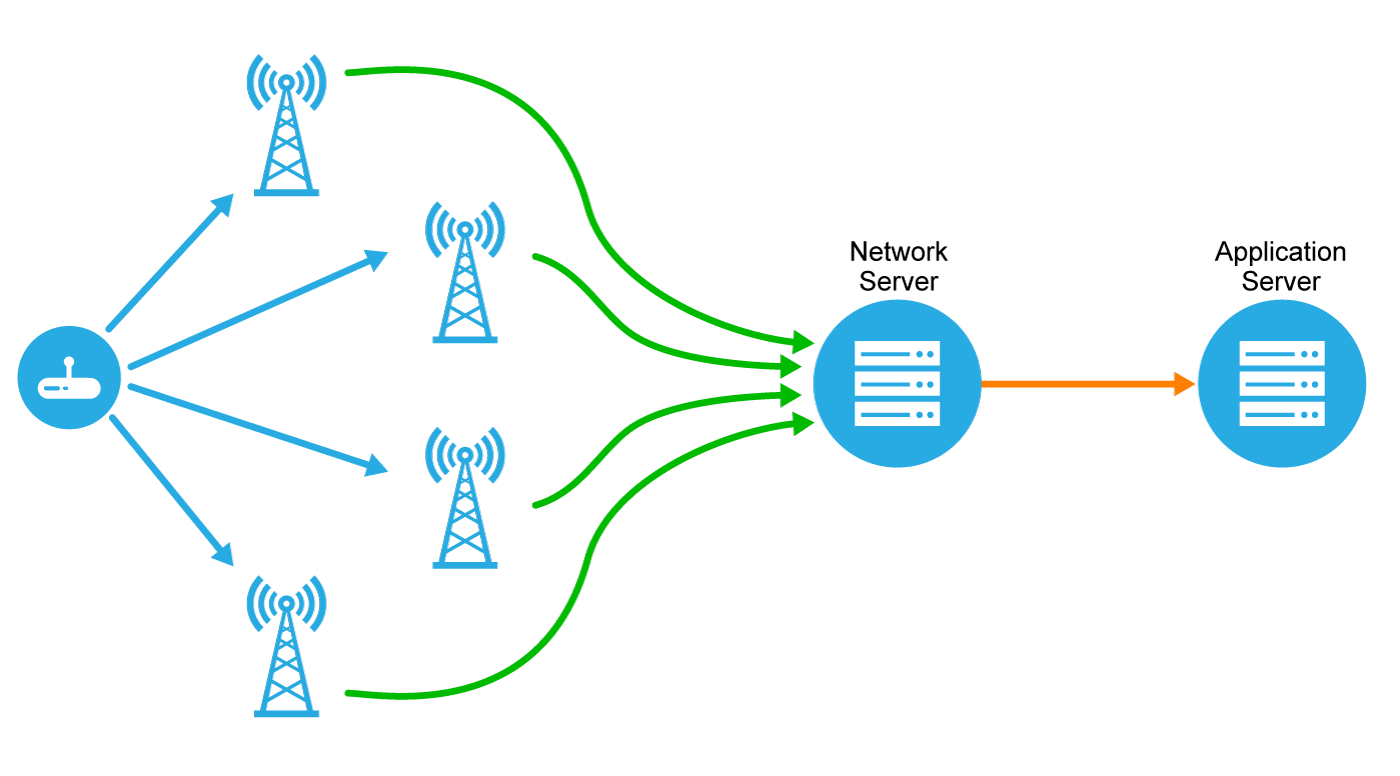
LoRaWAN Network Topology
Source: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/library/tech-papers-and-guides/lorawan-class-a-devices/
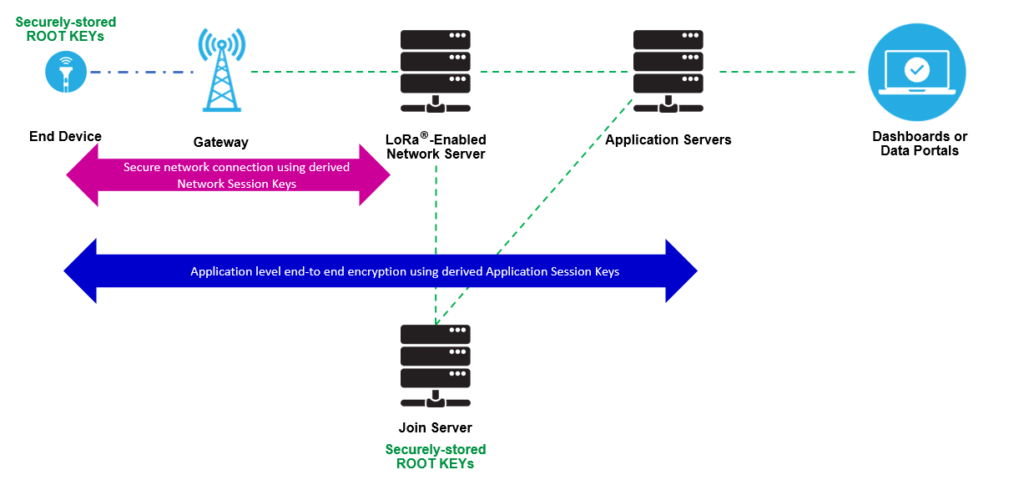
The LoRaWAN Network Server supports a Join procedure (via Join Server) to authenticate and setup the LoRaWAN network address and encryption keys (network and application session keys) for the devices. This is called “Over-the-Air Activation”, OTAA. An alternative is ABP – Activation by Personalization (ABP).
LoRaWAN – Join Server and Encryption Keys
Source: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/library/tech-papers-and-guides/lora-and-lorawan/
EveryNet Network Server
Let’s look at the frame log (operational history), as seen using the EveryNet Network Server (https://ns.us.everynet.io).
Frame Log
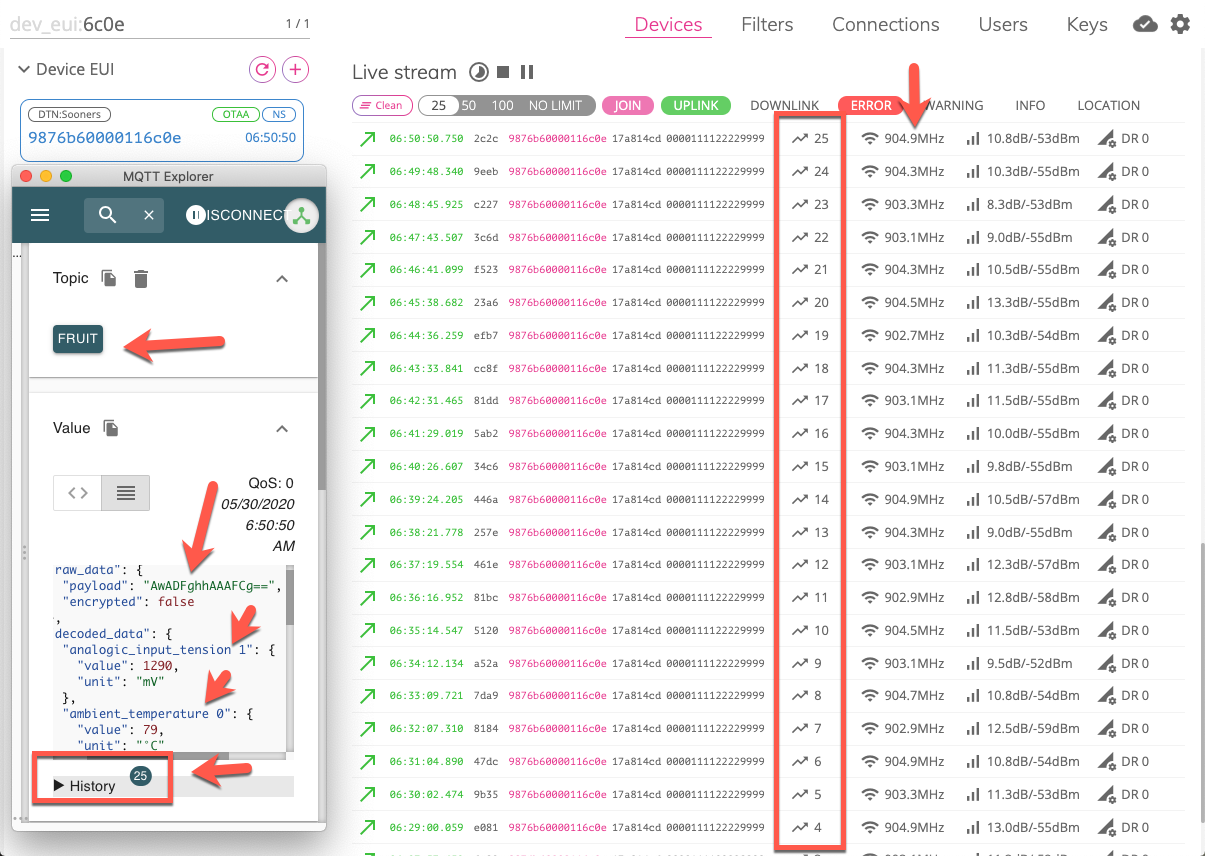
This image shows the Uplink history for a device at the EveryNet Network Server.
The left side of the image shows the payload as seen in the MQTT client (after decrypt and decode in CemTore.)
You can use the Network Server – Frame Log to track Join, LoRaWAN MAC commands, and basic device connectivity info.
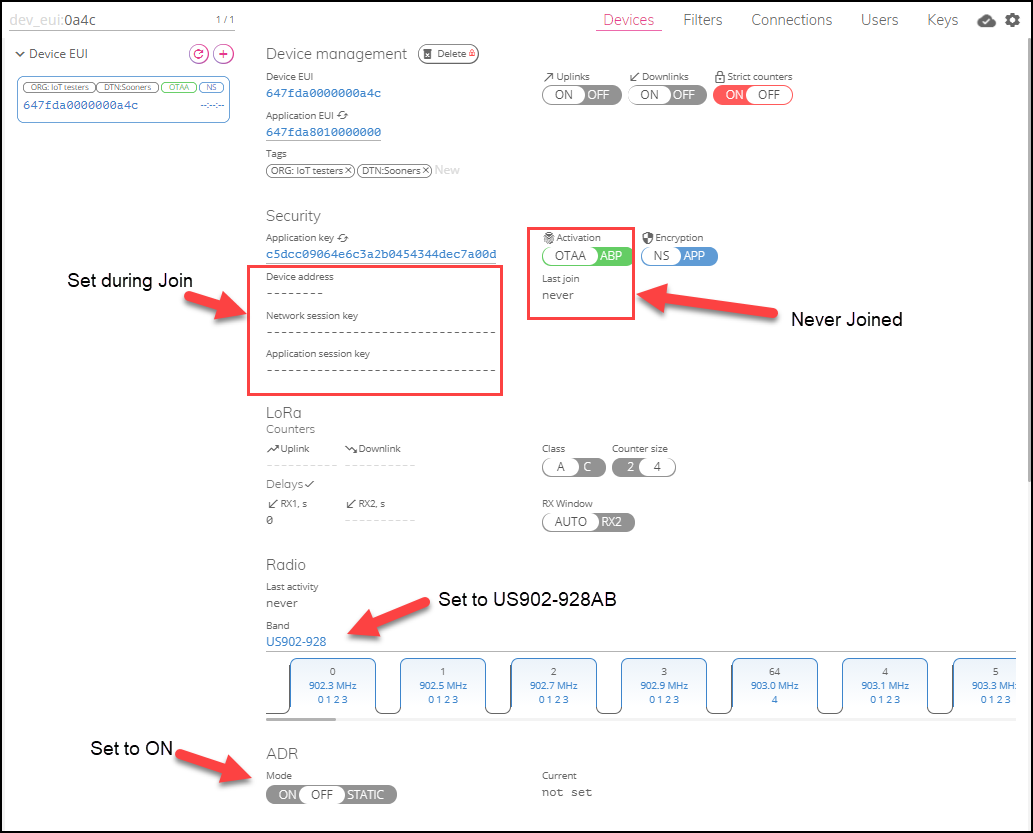
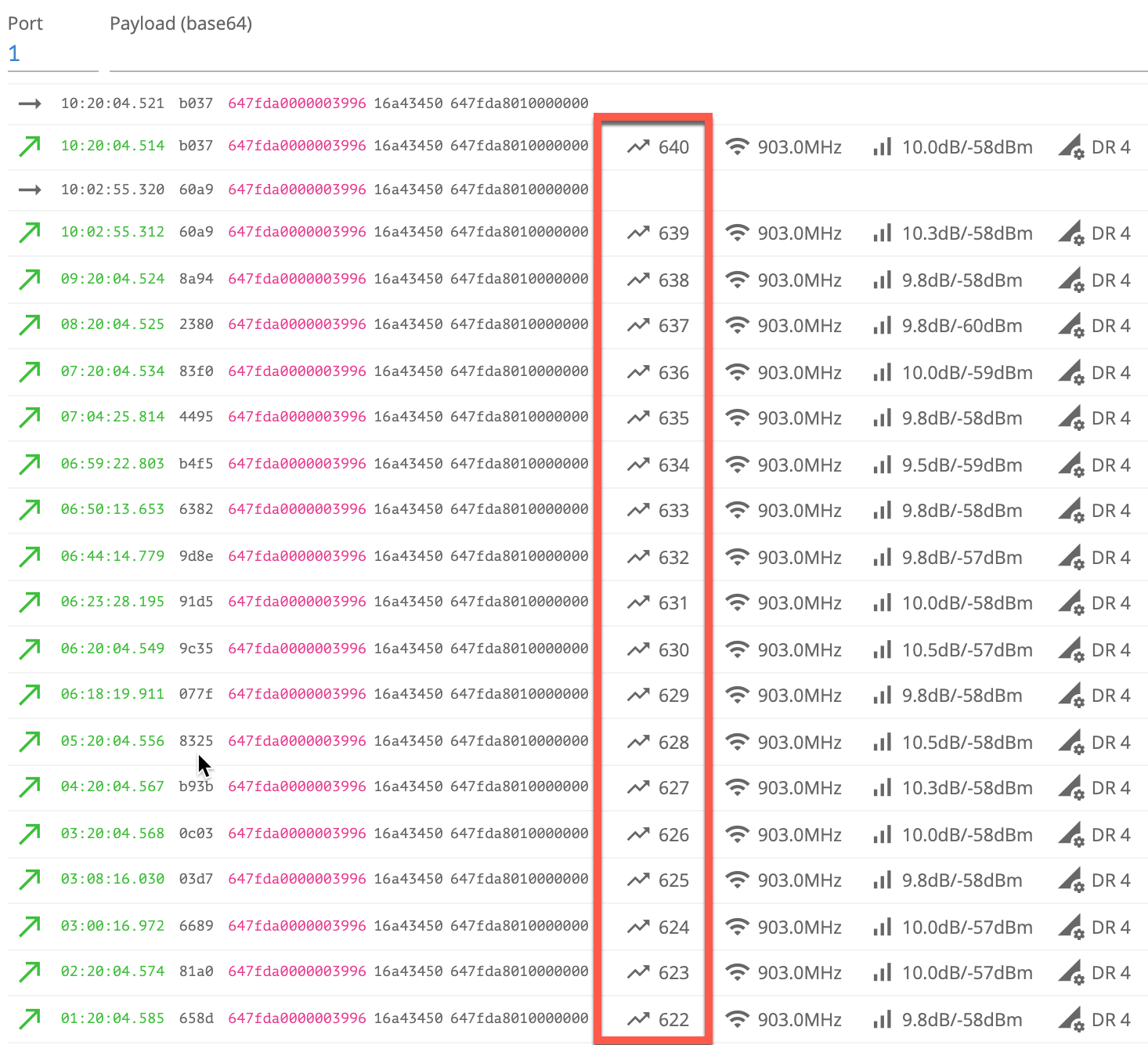
Uplinks from a Tektelic Smart Sensor